Ammazza! 28+ Verità che devi conoscere Cluster Random Sampling Example Situation: Cluster sampling, which, similar to the stratified sampling methodstratified random samplingstratified random sampling is a practical example.
Cluster Random Sampling Example Situation | It is a process which is usually used for market research when there is no feasible way to find information about a. For example, males under 30 similar to stratified random sampling , cluster sampling divides the sample into a large number of subgroups. Cluster sampling, which, similar to the stratified sampling methodstratified random samplingstratified random sampling is a practical example. Cluster sampling is a method that makes the most of groups or clusters in the population that correctly represent the total population in relation to one characteristic often used to define clusters is geography. Let's suppose that the bulbs come off the assembly line in boxes that each contain 20 packages of four bulbs each.
For example, it may not be possible to list all of the customers of a chain of. For example, a marketer may want to study the effectiveness of. Random sampling method can be divided into simple random sampling and restricted random sampling. Each of these random sampling techniques are explained more fully below, along with examples of each type. An overview of systematic random sampling, explaining what it is, its advantages and disadvantages, and how to create a systematic random sample.
Stratified random sampling is a method of sampling that involves the division of a population into smaller groups known as strata. Imagine that a researcher wants to understand more about the career goals of students at the university of bath. In this situation, the clusters (classes in our example) are randomly selected and then students within those clusters are randomly selected. Let's suppose that the bulbs come off the assembly line in boxes that each contain 20 packages of four bulbs each. For example, you may first choose districts from a list of all districts in. .example of a simple random sampling procedure could involve labelling each of the members of the source population on pieces of paper, and randomly than it would be to sample small numbers of animals from many clusters (as would be the likely situation if simple random sampling was used. Cluster sampling is a sampling method where populations are placed into separate groups. Simple random sampling (also referred to as random sampling) is the purest and the most straightforward probability sampling strategy. Random sampling method can be divided into simple random sampling and restricted random sampling. A random sample of these groups is then selected to represent a specific population. Use random cluster sampling when other methods are impractical. Cluster sampling is a probability sampling technique where researchers divide the population into multiple groups (clusters) for research. For example, males under 30 similar to stratified random sampling , cluster sampling divides the sample into a large number of subgroups.
Simple random sampling the elements are randomly selected from each of these strata. In this situation, the clusters (classes in our example) are randomly selected and then students within those clusters are randomly selected. Cluster sampling, which, similar to the stratified sampling methodstratified random samplingstratified random sampling is a practical example. Sampling without replacement is a method of random sampling in which members or items of the population using the same example above, let's say we put the 100 pieces of paper in a bowl, mix them up, and randomly select one. In these situations, you'll need to randomly select a few smaller groups to work with that are hopefully.

Cluster sampling is a probability sampling technique where researchers divide the population into multiple groups (clusters) for research. Cluster sampling is a sampling method where populations are placed into separate groups. Random samples are then selected from each stratum. In the case of cluster sampling, the selection of samples at random is done at various stages. For example, males under 30 similar to stratified random sampling , cluster sampling divides the sample into a large number of subgroups. Simple random sampling is sampling where each time we sample a unit, the chance of being sampled is the same for each unit in a population. In this sampling plan, the total population is divided into these groups (known as clusters). Random sampling method can be divided into simple random sampling and restricted random sampling. Cluster sampling, which, similar to the stratified sampling methodstratified random samplingstratified random sampling is a practical example. For example, consider an academic in other situations, however, it might be far more difficult. Each of these random sampling techniques are explained more fully below, along with examples of each type. Advertising in a particular city. If our population has 45% females and 55% males then our sample should reflect the.
Simple random sampling (also referred to as random sampling) is the purest and the most straightforward probability sampling strategy. In this sampling plan, the total population is divided into these groups (known as clusters). Many dissertation supervisors advice the choice of random sampling methods due to the representativeness of sample group and less room. For example, if we want to study what percent of the argentine population smokes, we. We record one or more of its properties (perhaps its color, number.
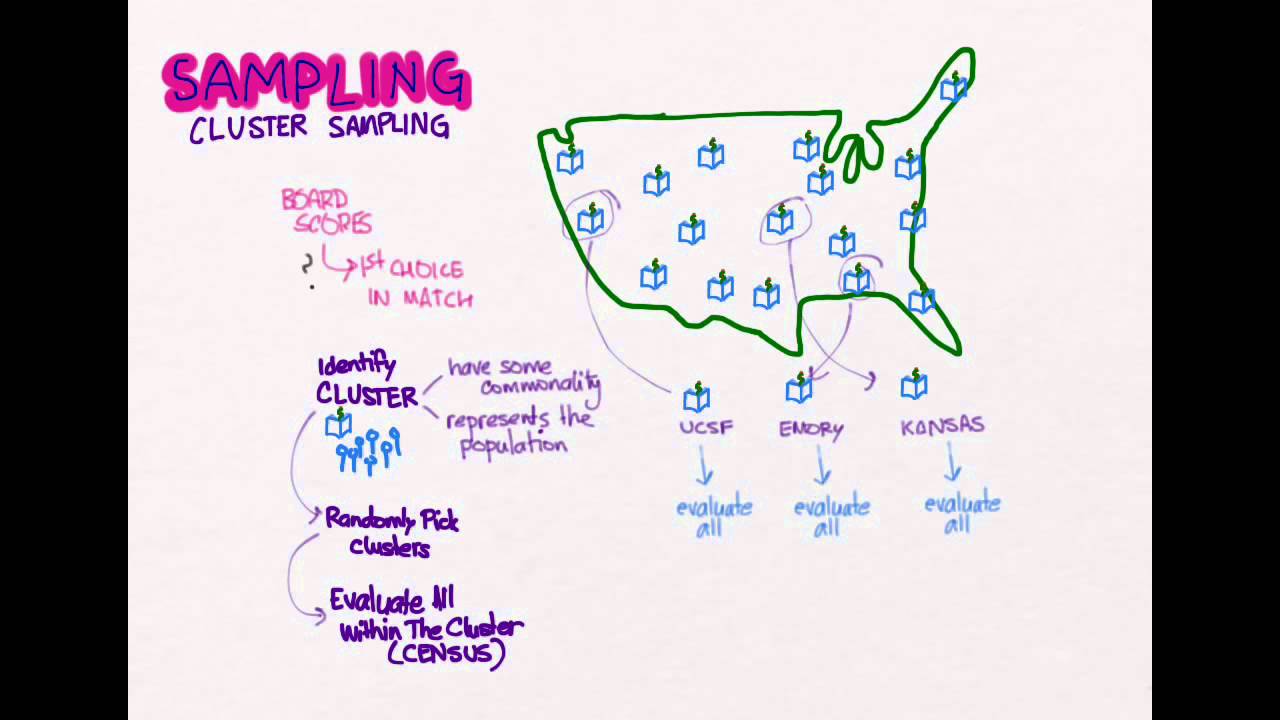
Out of ten tours they give one day, they #randomly choose 4 tour groups out of the 10 clusters = np.random.choice(np.arange(1,11), size=4, replace=false) #. Suppose a company that gives city tours wants to survey its customers. Collect data on each sampling unit that was randomly sampled from each group (stratum). Stratified random sampling is a method of sampling that involves the division of a population into smaller groups known as strata. Random sampling examples show how people can have an equal opportunity to be selected for something. If our population has 45% females and 55% males then our sample should reflect the. Stratified sampling works best when a heterogeneous population is split into fairly homogeneous. Simple random sampling is sampling where each time we sample a unit, the chance of being sampled is the same for each unit in a population. For example, males under 30 similar to stratified random sampling , cluster sampling divides the sample into a large number of subgroups. Cluster sampling is just a way to randomly choose smaller and smaller geographic areas until you get to a small enough area so that you can find or create a list of all households in order to do simple or systematic random sampling. The company wishes to conduct a survey to determine employee satisfaction based on a. Simple random sampling (also referred to as random sampling) is the purest and the most straightforward probability sampling strategy. A university newspaper reporter is interested in estimating the average number of hours dormitory residents spend studying.
Simple random sampling (also referred to as random sampling) is the purest and the most straightforward probability sampling strategy random sampling example situation. For example, you may first choose districts from a list of all districts in.
Cluster Random Sampling Example Situation: Cluster sampling refers to a sampling method that has the following properties.